

Such as entropy, temperature, heat capacity, and pressure. While the behavior ofĪ system is illustrated in terms of empirically defined thermodynamic variables The microscopic features of a system are not considered. Which energy is dispersed is called entropy.Ĭlassical thermodynamics was first developed. Thermodynamics has been to illustrate the distribution of a given amount ofĮnergy E over N identical system Definition Hence, the crucial problem in statistical That it is directly proportional to the natural logarithm of the number of Measure the entropy of ideal gas particles in which he explained the entropy Statistical basis by different scientists named Ludwig Boltzmann, Josiah Theories of Newton that heat was an indestructible particle having a mass. The transformation content in contrast to an earlier view that was based on the For example, the heat produced by friction. German physicist named Rudolf Clausius objects to the supposition that noĬhange occurs in a working body and gave this change a mathematical explanationīy interrogating the nature of the inherent loss of usable heat when work isĭone. However, itĭoesn’t tell us the effects of friction and dissipation. The concept of energy and its conservation in all processes. That both heat and light were indestructible forms of matter that are attractedĪnd repelled by other matter and he took this view from the Newtonianįirst law of thermodynamics, from his experiments on heat-friction expresses In the early 18 th century, Carnot tells us from a hot to aĬold body, motive power or work can be produced. Heat (caloric) decreases through a temperature difference i.e. The Motive Power OF Fire which suggested that in every heat-engines, whenever From theīasis of this work, in 1824 Lazare’s son Sadi Carnot published Reflections on Principles of Equilibrium and Movement in any machine represents moment lossesīy activities through acceleration and shocks of the moving parts.

HistoryĬarnot, a French mathematician suggested in his 1803 paper named Fundamental It relates to the number Ω of microscopic configuration which isĪlso known as microstates which are consistent with the macroscopic quantitates
#Entropy change formula free#
The Gibbs free energy equation is ΔG = ΔH - (T * ΔS) and isothermal entropy change of an ideal gas is ΔS = n * R * ln(V₂/V₁) = - n * R * ln(P₂/P₁).
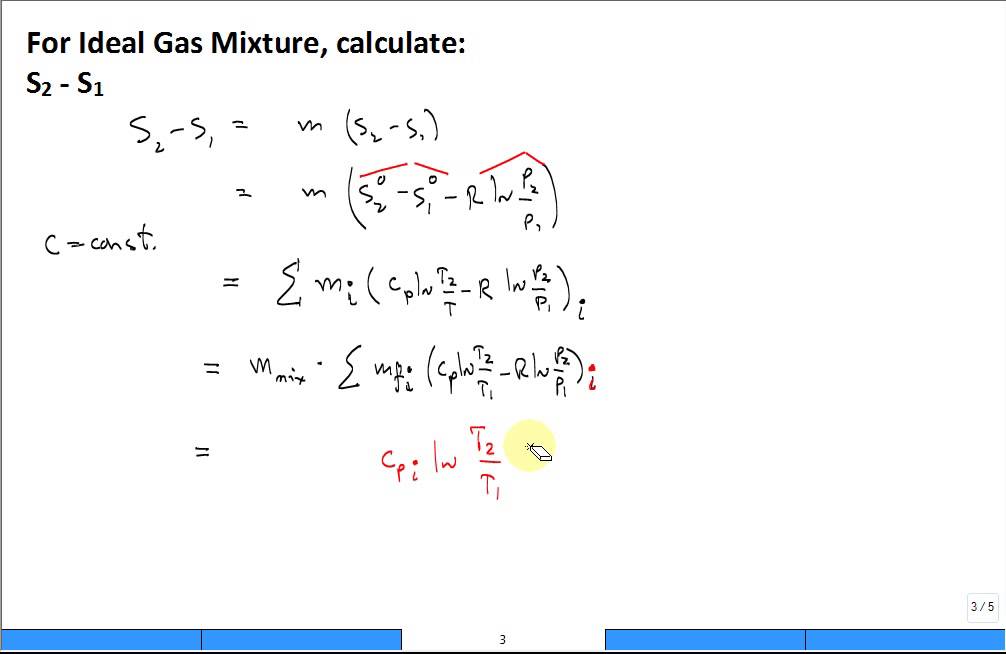
The entropy change formula for chemical reactions is ΔS reaction = ΔS products - ΔS reactants. The change in entropy measures the difference between the entropy of products and reactants. The Shannon entropy measures the entropy of an object or the system is a measure of the randomness in the system.ģ. The second law of thermodynamics states that the disorder of a system is always increasing.

It can be explained in thermodynamics and statistics. What is a simple definition of entropy?Įntropy is a measure of randomness or disorder of a system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
